From Code to Intent: The Rise of AI-Powered Software Creation Tools
How Codex, Replit, Cursor, and other tools are shaping the next frontier of autonomous app development across Web2 and Web3.
The emergence of OpenAI’s new Codex agent has reignited global interest in "vibe coding"—the dream of writing software by simply describing what you want. In this new era, the keyboard is optional. The cursor listens, understands, and composes.
Vibe coding tools—once limited to autocomplete widgets—are now evolving into multi-agent orchestration layers that understand user goals, reason across context, and autonomously build and deploy full applications.
In this blog-research hybrid, we:
Compare the most prominent vibe coding tools (Codex, Cursor, Replit AI, DevGPT, etc.)
Highlight their unique strengths, gaps, and architectural differences
Analyze the structural evolution of the vibe coding stack
Identify emerging patterns: verification, project awareness, and autonomous planning
Discuss the implications for the future of developer tooling, no-code platforms, and intelligent agents
We close with a forward-looking vision: a world where platforms like Questflow serve as orchestration layers for AI agents capable of building and deploying fully integrated Web3 applications—just from a user prompt.
What Is Vibe Coding?
"Vibe coding" refers to a development paradigm where software is written not line-by-line, but by expressing intent. The system—aided by AI—takes on the role of an assistant, collaborator, or even autonomous engineer.
This idea is not new. From Scratch and IFTTT to Copilot and GPT-4, we’ve seen decades of effort to lower the barrier to software creation. But only recently have we begun to reach the inflection point where LLMs can:
Understand multi-turn instructions
Write high-quality code across frameworks
Execute, verify, and iterate without human intervention
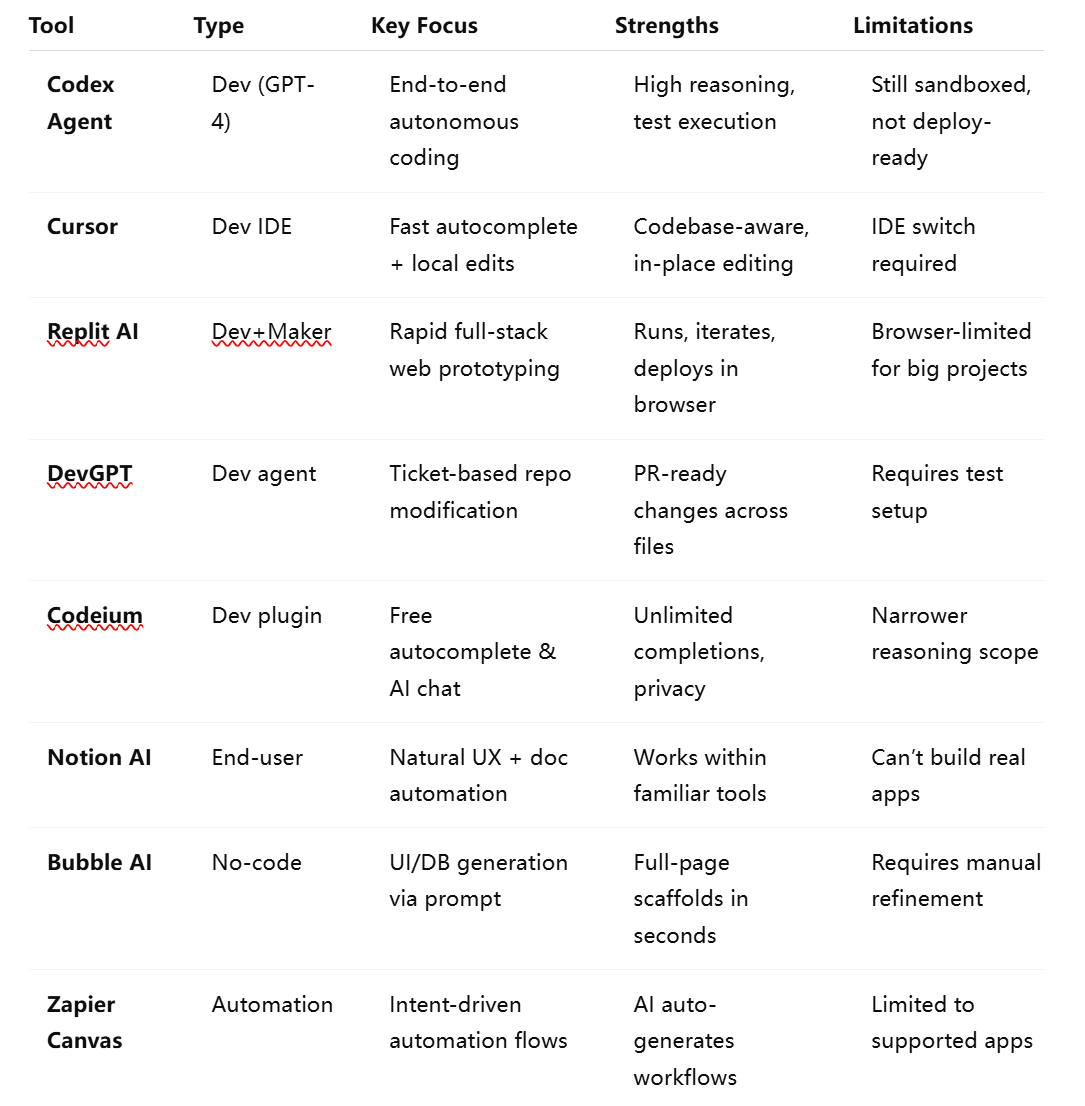
Comparing Vibe Coding Platforms
Below, we outline the core features, strengths, and limitations of major vibe coding platforms:
Anatomy of a Vibe Coder: Technical Stack
Modern vibe coding platforms are converging on a modular stack:
What Makes a Good Vibe Coding Platform?
Across tools, we see a few dimensions emerge as key to developer trust and long-term viability:
Current Challenges in Vibe Coding
While vibe coding has made rapid strides, major hurdles remain:
Debugging complexity: Users often lack visibility into AI’s reasoning when it produces faulty code
Multi-agent orchestration: Most tools still rely on a single-agent model. Coordination is fragile
Incomplete verification: Testing is limited or superficial, especially in no-code contexts
Codebase-scale reasoning: Understanding 50k+ LOC projects is still unreliable, though improving with larger context windows
Security & compliance: AI output may bypass org policies or contain subtle vulnerabilities
The Path Ahead: What the Next 12–24 Months Hold
Key trends we expect in the coming product cycles:
Agent swarms: Multiple cooperating agents with defined roles (writer, reviewer, tester, deployer)
Conversational debugging: Users interact with failed code like a conversation — “Why didn’t this work?”
Self-deploying agents: From prompt to deployed dApp, with full CI/CD managed by agents
Trust dashboards: Visualize confidence scores, test coverage, and agent decision trails
Contextual LLMs: Fine-tuned models that adapt to project norms, repo style, and team structure
Cross-modal design: Build from sketches, voice, or screenshots — not just text
Prospects of Composability between Vibe Coding and Web3
Questflow is emerging as a platform purpose-built for agent orchestration across Web3 protocols. It supports multi-agent workflows, secure execution, and modular integrations across onchain services.
In the future we imagine:
A user in a Web3 community posts an idea: “We should do a community raffle tied to NFT holders.”
Another user sees it and describes it to Questflow: “Make a weekly raffle for all users who hold NFT X and meet activity Y.”
Questflow activates:
Retrieves holder list via Alchemy agent
Evaluates onchain behavior via Dune or Flipside agent
Generates a smart contract via Solidity agent
Simulates + verifies via audit agent
Deploys to Base or Optimism
All coordinated by MAOP—Questflow’s Multi-Agent Orchestration Protocol. This is the vibe coding of Web3: AI-native composability meets permissionless infrastructure. Questflow is poised to become the Zapier meets GitHub Copilot for blockchain automation.
Conclusion: Beyond Vibe Coding, Toward Agent-Powered Design
With Codex, Cursor, Replit, and others pushing toward autonomous coding, and platforms like Questflow bringing agents to Web3, we’re entering a phase where intent becomes design.
The next generation won’t ask “how do I build this?” but rather, “how do I describe it well enough that it builds itself?”
That’s the new interface: idea → AI → outcome.
And platforms like Questflow are bringing that to every DAO, community, and onchain builder around the world.